|
|
本帖最後由 -終場ソ使者- 於 20-6-2011 19:32 編輯
你唔明,係正常既,我估你對statistics既認識都會CE程度,
我係讀m2,不過有研究過呢個graph,俾d意見啦(我係呢方面冇接受過嚴謹既訓練)
如果你有讀AL chem,應該會見過1個probability distribution of electrons,姐係electrons圍繞住個nucleus出現既prob.(某d位置出現electrons既prob.係特別大,某d位置既prob.特別細)
又舉個例,某某地區既人既平均IQ係107,standard deviation係5,當數據夠多既話,就會plot到1條graph,呢條graph既樣就好似一條intestinal villus咁,不過係左右對稱,比較完整既,而呢條graph既function正確d既寫法係
 (呢個graph係叫做normal distribution,F5 core math有教) (呢個graph係叫做normal distribution,F5 core math有教)
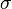 =standard deviation =standard deviation
 =mean =mean
至於 只係for standard normal distribution 只係for standard normal distribution
(core math有教, 呢個interval內所佔有總數既%係68%) 呢個interval內所佔有總數既%係68%)
而個area係用黎搵一個interval入面所佔total area既%
呢個graph係點黎,你就要多謝某某數學家/統計學家啦,係佢地好辛苦地plot出黎
上述講到個area in an interval代表該interval既%
即
d constant咁無稜兩可有咩意義呢?就係plot呢條graph既人既聰明之處,因為

如果個個constant  係其它既話,個area in interval 係其它既話,個area in interval  就唔係=1 就唔係=1
所以個聰明人就將佢設計成area in interval  =1啦 =1啦
舉個例子,如下圖

紅線既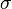 =4, =4, =35 =35
紫線既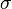 =2, =2, =37 =37
所以你見到當佢既x value= ,就會遇到個max. value,而 ,就會遇到個max. value,而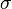 就係決定佢既"粗幼程度"( 就係決定佢既"粗幼程度"(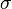 大,佢會"粗"d, 大,佢會"粗"d,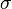 細,就會"幼"d) 細,就會"幼"d)
正因為佢既area in interval  =1,所以當 =1,所以當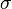 增加,area不變,"高度"就會下降(因為"粗"左),所以個"高度"並不反映d咩架! 增加,area不變,"高度"就會下降(因為"粗"左),所以個"高度"並不反映d咩架!
不過個問題係,個f(x)既面積點計呢?
放心,係唔洗要你計,對表就得,個function係比你applied番,冇乜實際用處
PS:以上內容我只係用左幾個小時既研究,有錯莫怪 |
|